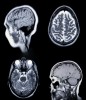
As part of the diagnostic procedures, specific metabolic processes in the body are visualized by means of nuclear medicine. This occurs when the gamma rays of the administered radiation dose in the body decompose in a way that the rays can be accurately measured and graphed. In a location where especially many gamma rays were released, differences in brightness refer to certain metabolic processes in the body, as it is, for example the case with cancer metastases.
The most common therapeutic uses of the nuclear medicine include the treatment of cancer, heart diseases, rheumatic diseases, thyroid disorders and the examinations of the brain. Also inflammatory processes, for example in joints, can be treated by means of nuclear medicine.
The radioactive substances are transported either via a blood injection, the intake of tablets or by aerosol gases to those organs that have to be treated. The radioactive quantity or radiation exposure, which is supplied to the person during the procedure is very weak, and corresponds more or less to a larger X-ray examination. Usually, no consequential damages are to be expected.