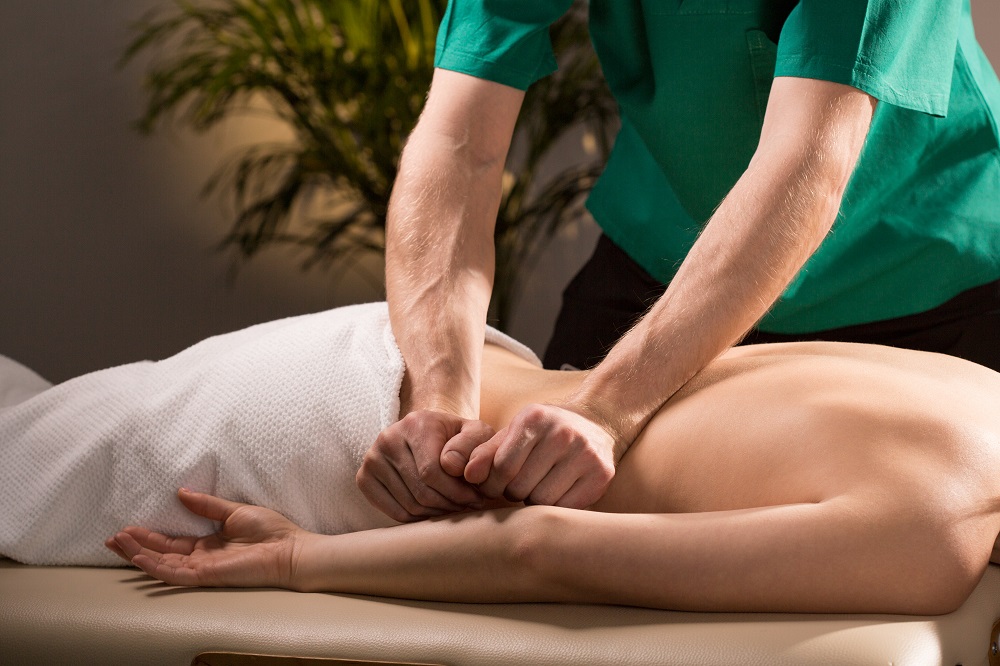
The therapeutic approach focuses e.g. on the holistic view of blockages in the spine or joints, i.e. on the whole body. Specific and targeted grips resolve the blockades and mobilize the joints. In principle, functional disorders of the musculoskeletal system are healed holistically. Both clinical examination and treatment are performed exclusively by hand. Thus neither invasive nor drug therapies are used.
The applications that promote mobility include, for example, special smoothly performed and frequently repeated stretching or manipulative applications in order to loosen strong, impulsive and quick movements of blocked joints. The therapist provides a targeted nerval stimulation to relax tense muscles that block the joint. Normally, it can be done only with a minimum of force.
In manual therapy, a distinction is made between chiropractic and osteopathy. Chiropractic is based on the idea that the nervous system is the most important factor for health and that most diseases are caused by spinal subluxations, which are responsive to grips on the spine. The chiropractic is only responsible for the recovery of impaired room-to-move of joints.
In contrast, osteopathy was already recognized by conventional medicine as an independent medical area in 1874. Osteopathy works with the therapeutic approach of using grip techniques that remove blockades of nervous, blood and lymphatic systems. In this way it can influence almost all life processes of the body.